Bio Gallic Acid GA-100 BIO
Creating from and for nature
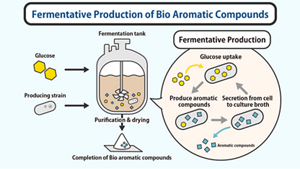
Kao has developed a fermentative production technology that uses microorganisms to produce gallic acid from glucose. Gallic acid is a basic raw material used in a wide variety of business fields, including electronics, industry and food.

Gallic acid is widely used as a semiconductor-related material in electronic devices such as personal computers and smart phones, and as anti-rust for boilers. Despite its industrial importance, it is found in gallnuts and tara, the production area is limited, and yields are easily affected by weather conditions.
Kao focused on the fermentation technology using glucose and continued to develop a practical production technology and succeeded in introducing multiple gallic acid production pathways into Coryneform bacteria and inhibiting the metabolic pathway of by-product residence.
With this technology, we have established a new supply chain that enables highly efficient production and stable supply of gallic acid.
Features of Gallic Acid GA-100 BIO
-
Features
- 1Stable supply unaffected by seasonal fluctuations
- 2Environmentally friendly manufacturing method
- 3No limitation of country of origin
Image of fermentative production of Gallic Acid
Main physical properties
| Properties | White to light brown yellow crystals or crystalline powder |
| Purity | > 99% |
| Loss on drying | < 10.5% |
| Ignition residue | < 0.10% |
| Heavy metal as Pb | < 20ppm |
Application examples

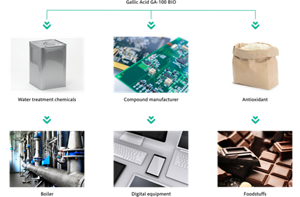
Case studies
Application to water treatment chemicals for boilers
Kao has confirmed that GA-100 BIO, Kao's gallic acid, exhibits performance comparable to that of current products in a comparative study of the anti-corrosion effect on steel chips using a small once-through boiler. Kao has received the notification from the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that "Gallic Acid and its salts are used in water boilers, at a level of 100 ppm, at temperatures exceeding 160℃ to prevent corrosion. The steam generated from the water boiler is then used to heat the food processing reactor's outer jacket. Based on analyses, the Gallic Acid and its salts are not present in the steam down to the part per million level. Furthermore, the steam is used in the food processing reactor's outer heating jacket (closed system) . Therefore, the steam with any possible residual gallic acid will not be in direct or indirect contact with food or food contact surfaces". This encourages to promote not only domestic development but also overseas expansion.

Environmental Considerations
Stability of production
Diversification of Supply Chain


If you have any questions or require additional information about GA-100 BIO, please use the form below.
Bio-Conversion
enables the utilization of non-edible biomass
Saccarification enzyme CRESCENTIS™

Bio-Process Agents
The process of fermentation leads to success.
Bioprocess Agents


